Implemented Algorithms¶
Dynamic graph embedding algorithms aim to capture the dynamics of the network and its evolution. These methods are useful to predict the future behavior of the network, such as future connections within a network. The problem can be defined formally as follows.
Consider a weighted graph $G(V, E)$, with $V$ and $E$ as the set of vertices and edges respectively.
Given an evolution of graph 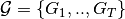 , where
, where 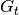 represents the state of graph at time
represents the state of graph at time 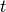 , a dynamic graph embedding method aims to represent each node $v$ in a series of low-dimensional vector space
, a dynamic graph embedding method aims to represent each node $v$ in a series of low-dimensional vector space 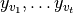 by learning mappings
by learning mappings 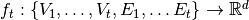 and
and 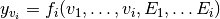 .
The methods differ in the definition of
.
The methods differ in the definition of 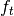 and the properties of the network preserved by
and the properties of the network preserved by 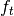 .
.
There are various existing state of the art methods trying to solve this problem that we have incorporated and included them in this python package including:
Optimal SVD: This method decomposes adjacency matrix of the graph at each time step using Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) to represent each node using the $d$ largest singular values.
Incremental SVD: This method utilizes a perturbation matrix capturing the dynamics of the graphs along with performing additive modification on the SVD.
Rerun SVD: This method uses incremental SVD to create the dynamic graph embedding. In addition to that, it uses a tolerance threshold to restart the optimal SVD calculations and avoid deviation in incremental graph embedding.
Dynamic TRIAD: This method utilizes the triadic closure process to generate a graph embedding that preserves structural and evolution patterns of the graph.
AEalign: This method uses deep auto-encoder to embed each node in the graph and aligns the embeddings at different time steps using a rotation matrix.
dynGEM: This method utilizes deep auto-encoders to incrementally generate embedding of a dynamic graph at snapshot
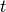 .
.dyngraph2vecAE: This method models the interconnection of nodes within and across time using multiple fully connected layers.
dyngraph2vecRNN: This method uses sparsely connected Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) networks to learn the embedding.
dyngraph2vecAERNN: This method uses a fully connected encoder to initially acquire low dimensional hidden representation and feeds this representation into LSTMs to capture network dynamics.